Diabetes mellitus is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism. Its essence lies in the fact that the body cannot properly absorb glucose. The disease is divided into two types.
In type 1 diabetes, the abnormal cells in the pancreas don't produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels stable.
Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% of all diagnosed cases. It occurs when the insulin produced is not felt by the body; H. there is resistance to this.

Dietary Guidelines for Diabetes
The main principle of dieting for diabetes is not to reduce the amount of any type of food, but to properly rebuild the entire diet and stick to it for the rest of your life.
From a biological point of view, food is a source of vital vitamins, trace elements and necessary energy.
With diagnosed diabetes, they try to reduce the amount of this energy that a person receives from food. Too much of it is the cause of obesity, which only aggravates the course of the disease.
The main components of the diet in diabetes are fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the body's main source of energy. Their share is about 50% of the daily intake.
There are three groups of carbohydrates:
- The ones that don't need to be counted. These are foods enriched with plant fiber (the exceptions are legumes and potatoes due to their high starch content).
- Slow-digesting carbohydrates (cereals, fruits, vegetables).
- Quickly digestible carbohydrates (sweets of all kinds).
To calculate the insulin dose, the amount of carbohydrates consumed is taken into account using the "bread unit" system. One bread unit (XU) corresponds to 10-12 g of carbohydrate. Entire tables have been created to accurately determine the approximate content in a particular type of food.
The required number of bread units is determined by the person's weight and level of physical activity. Approximately this figure corresponds to - 15-30 XE per day.
Using the XE table, which adjusts the blood sugar level before and after meals, you can calculate the required dose of insulin, which controls the level of sugar and the process of carbohydrate metabolism itself. In the absence of tabulated data, the "hand and plate rule" applies when determining the size of the products eaten based on hand and plate size.
Another indicator that plays an important role in organizing diabetic nutrition is the glycemic index (GI). It helps control carbohydrate metabolism and determines the most beneficial dietary option. It was first introduced by Canadian specialist A. Jenkinson in the early 1980s.
The GI of glucose itself is 100 units. The earlier its level rises after eating, the higher the index. GI - an indicator of the degree of usefulness of the product. Its low value indicates that the product is recommended for people with diabetes. A high GI score indicates useless calories. Low GI foods slowly increase blood sugar levels. And when you're high, on the other hand, it quickly increases glycemia. The first group includes vegetables, fresh fruits, whole grain breads, seafood, eggs, etc. The second group includes muffins, candy, soda pop, packaged juices, etc. Knowing the main criteria of a diabetic diet will allow you to regulate the course of the disease, quality of lifeimprove such patients.
Features of the diet for diabetes

Patient studies have proven that strict adherence to a diet and proven eating patterns are essential to successfully managing diabetes mellitus, minimizing potential complications, and maintaining good health.
In people with diabetes, it is necessary to pay attention to a number of features that regulate nutrition, regardless of the severity of the disease and the methods of treatment.
A person must be aware that whatever treatment is chosen for them, their success depends primarily on the dietary culture.
The nutritional regimen is selected for each patient individually, depending on weight, age and level of daily physical activity.
The goal of the diabetic diet is to control the level of glucose and keep it at an optimal level according to generally accepted norms. It is important that the diet is balanced and enriched with a range of vitamins and minerals. It is obliged to ensure the supply of the necessary energy so that the patient's body weight is close to ideal indicators and remains stable for a long time. The diet must correspond to the principles of a rational diet.
Diet in type 1 diabetes

Nutrition experts agree that the diet plan for type 1 diabetes must be balanced and based on the postulates of proper nutrition, just as it is for people who do not have the disease. Since there is no ideal diet for diabetics, these patients must pay close attention to the ratio of carbohydrates, fats and proteins entering the body. This will help you adjust your diet. A diabetic diet does not mean completely avoiding certain foods, but you should consider how one or the other product affects blood sugar.
Recommendations for the amount of food consumed are as follows:
- Reduce the amount of packaged juices and drinks that raise blood sugar levels. Low-sugar drinks and special diet liquids are recommended for consumption;
- You can't completely eliminate carbohydrates from your diet. Their absence, in combination with insulin treatment, can significantly reduce sugar levels, which negatively affects overall health;
- eat as many low GI vegetables as possible;
- Reduce the amount of fast food and fast food.
A large proportion of patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes report the effectiveness of a low GI diet. This helps avoid sudden swings in blood sugar after a meal.
An important aspect of planning is calculating the amount of carbohydrates. He pays particular attention to diabetics who treat their diet responsibly. With the right calculations, you will learn exactly what dosage insulin should be and get relief in choosing the products you need.
Another popular method of insulin therapy is the basal bolus.
It consists of taking a bolus immediately before a meal to regulate optimal glucose levels within acceptable limits. Such a diet provides more flexibility when choosing a diet and allows you to independently adjust the required dose of insulin depending on the amount of carbohydrates consumed.
Diet in type 2 diabetes

Adherence to a healthy diet to reduce body weight is the main requirement. Being overweight has a significant impact on the course of the disease and the development of insulin dependence. In order for the fight against excess weight to be successful, you must follow all the recommendations.
Diet for type 2 diabetes has three main principles:
- The use of vegetables.Their number is determined by the patient's age, gender and level of physical activity. Women who train for 30 minutes should include about 500 g of such products in their diet. With more intensive sport, the amount of vegetables increases to 800 g, men should eat 600 and 1000 g accordingly.
- unsaturated fats. Their presence in the shopping basket helps regulate cholesterol levels and minimizes the likelihood of cardiovascular diseases, which are integral companions of diabetes. Such fats can be found in nuts, mackerel, tuna, avocados, olive oil, etc.
- Exclusion of processed foods.Refusal has a beneficial effect on the health of diabetics, which has been repeatedly confirmed by doctors. As a rule, such foods have a long shelf life thanks to special additives. It has a high GI. Its constant use negatively affects the general condition of the body of patients with diabetes.
As with type 1 diabetes, people with type 2 are advised to follow a low-carb diet and include low GI foods in their diet. This helps reduce blood sugar spikes. In order to determine how well the diet is composed, the number of sugars before and after meals must be constantly monitored. The data obtained shows how the body reacts to the chosen diet. If the efforts made do not give positive results, then the introduction of special antidiabetic drugs should be considered.
Also, people with type 2 diabetes should not bypass the basal-bolus diet. It keeps your glucose levels at optimal levels and improves overall health.
Allowed and forbidden foods in a diabetic diet

Carbohydrates are one of the most important sources of fat. People with diabetes need to use them with caution, but it is not recommended to completely exclude them from the diet, since all dietary components are important for the normal functioning of human organ systems. Nutritionists advise reducing the amount of fast carbohydrates and increasing the amount of slow ones.
Fast carbohydrates are found in foods such as:
- baked goods and sweets;
- Pasta;
- Potato;
- Fast food;
- Strength.
Vegetables and other foods of plant origin are rich in Slow Food. It is she who will improve health.
The diet menu for diabetes should include:
- various types of cabbage (Brussels white broccoli);
- Seaweed;
- Tomatoes;
- greens and onion;
- green beans;
- Mushrooms;
- cucumbers and celery;
- eggplant etc.
Garlic, beets, nuts, fish, avocados, etc. help lower blood sugar levels. The list of allowed foods on the diet is quite extensive. They are characterized by a low GI and high levels of healthy fiber, which helps reduce the risk of glycemia. Thanks to their action, glucose enters the blood in minimal quantities, and the presence of a large number of vitamins and trace elements helps to normalize the work of all vital body systems.
The list of prohibited foods in a diabetic diet is as follows:
- all confectionery, white flour muffins;
- Honey;
- various pickles and freshly made juices;
- condensed milk;
- Canned goods;
- syrups;
- fatty meat and fish;
- potatoes, rice;
- foods high in trans fat;
- semi-finished products.
sweeteners for diabetes
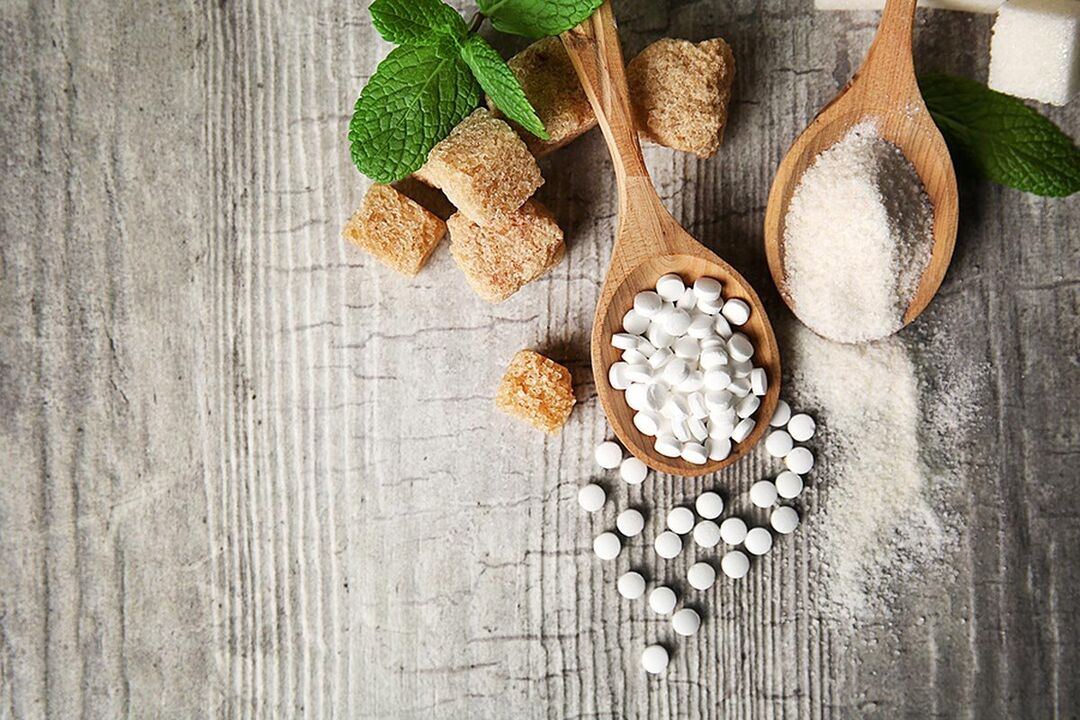

For people with diabetes, there is an alternative that allows you to replace regular sugar with special dietary supplements. They are divided into two categories: those who participate in the exchange processes and those who do not.
The most popular sweetener is fructose. It is made by processing fruits. Unlike regular sugar, it is much sweeter and has a low GI. Its use does not entail jumps in blood sugar levels. Natural substitutes also include sorbitol (found in apples, rowanberries and other fruits), erythritol ("melon sugar"), stevia (obtained by processing a plant of the same name).
Industrial sweeteners include sucralose, aspartame, saccharin, cyclamate, etc. The market for such additives is mainly represented by products of artificial origin.
Contraindications for diabetes
The main contraindication for diabetes mellitus of any type is the strict restriction of the intake of carbohydrates, which have an extremely negative effect on the level of glucose in the human blood. It is forbidden to eat sweets and ice cream and drink sugary drinks. Under control is the use of baked goods, honey. When glucose levels are high, exercise should be restricted. Under the ban are alcoholic and low-alcohol beverages, which also cause glycemia, which is accompanied by fainting, increased sweating and weakness. Patients with problems with the organs of vision should refrain from visiting the bath and sauna. High temperatures provoke the bursting of small blood vessels.
Diabetes is a serious disease that should not be taken lightly.
Diet for diabetes: menu for the week

Various menus have been developed for diabetics. One of the most common diet options for diabetes is menu number 9.
The simplest diet for a week might look like this:
- breakfast- an omelette with asparagus or buckwheat porridge, oatmeal on the water, black tea.
- dinner- Beans, beetroot, pickle, allowed vegetable stew, eggplant, raw carrot salad, apple.
- Afternoon tea- Rye bread, cottage cheese, kefir.
- dinner- stewed mushrooms, baked salmon fillet or boiled fish, stewed cabbage.
Less salt is recommended for cooked foods. Doctors advise keeping a special diary in which you need to write down everything that was eaten and in what quantity.
Recipes for a diet for diabetes
The list of allowed products includes beans and cottage cheese. On the Internet you can find a large number of recipes for a diabetic diet, which will make the diet varied and interesting.
bean pie
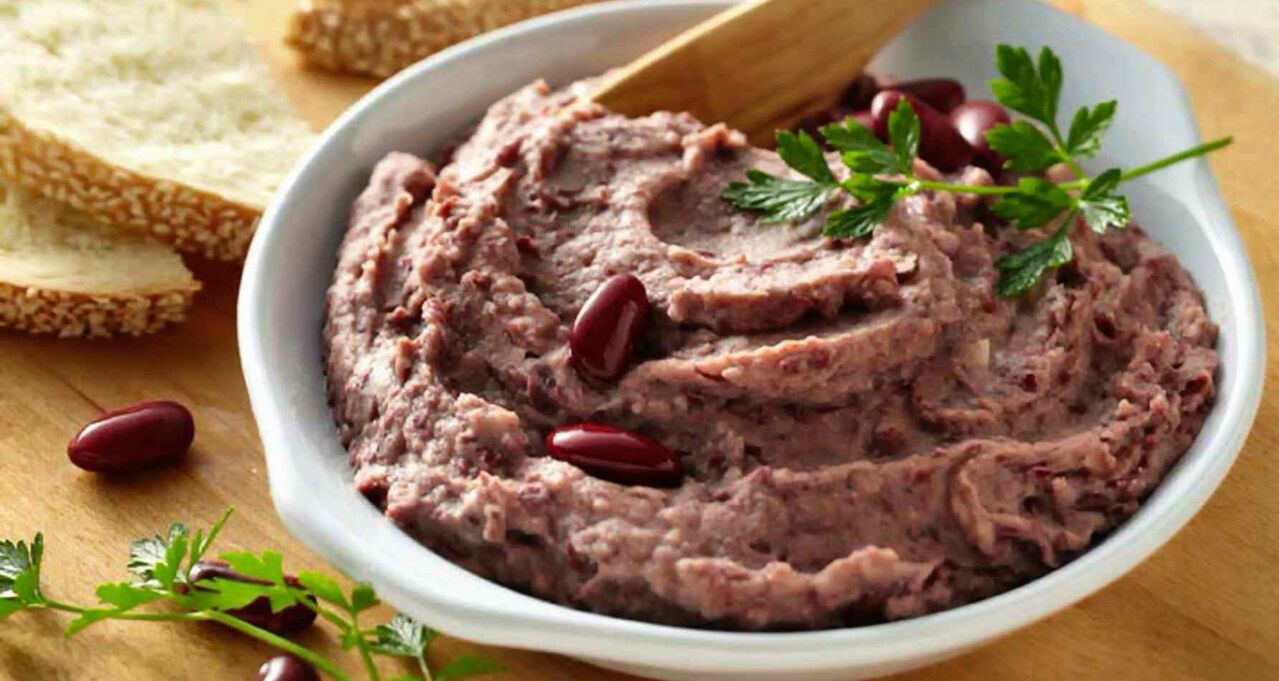

Drain excess liquid from canned beans. Grind the product with a blender to a homogeneous consistency. Finely chop the onion and sauté a little until translucent. grind walnuts. Peel the pomegranate seeds. Mix the bean mass with the remaining ingredients, salt. Delicious and healthy pie is ready to eat.
Cheesecake with tomatoes
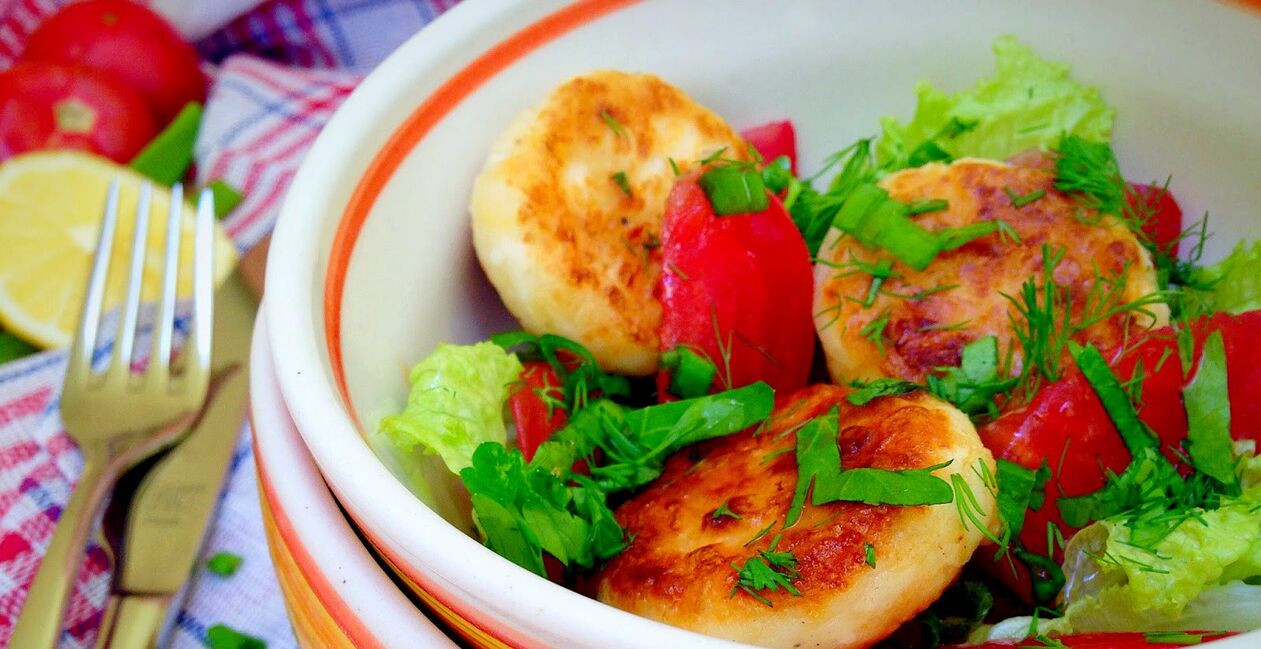

In a bowl, mix cottage cheese, egg, add oatmeal and spices. Rinse tomatoes in boiling water, cut into slices. Stir the quark mixture until smooth, form the cheesecake with wet hands and fry in a frying pan with the addition of olive oil. The dish is served with sour cream.
Diet for diabetes: reviews of nutritionists
Nutritionists have many years of experience in treating diabetes of any type by introducing a strict diet. Despite similar treatment tactics, different diets have their own individual characteristics. The comments of nutritionists are such that an individual diet plan for diabetes should be selected for each individual patient. Doctors agree in one opinion - successful treatment of diabetes is impossible without a correct and competent approach to dieting.